
| Home > CF Guidelines > Bowel & Nutrition > Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy |
 |
CF Guidelines - Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy |
||||||||
| Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy (P.E.R.T): | ||||||||
| Approximately 90% of CF patients re pancreatic insufficient and will need pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy to prevent malabsorption, poor growth, poor weight gain and deficiencies in fat soluble vitamins. If there are clinical signs of malabsorption, pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy should be started as soon as the diagnosis of CF has been made and confirmation of pancreatic insufficiency should be undertaken by measuring the level of faecal pancreatic elastase. In the absence of clinical signs of malabsorption pancreatic insufficiency should be confirmed before commencing pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy. | ||||||||
| Faecal Pancreatic Elastase Levels: | ||||||||
- |
Normal - > 200mcg/g of stool | |||||||
- |
Mild/Moderate pancreatic insufficiency - 100mcg/g - 200mcg/g of stool | |||||||
- |
Severe - < 100mcg/g of stool | |||||||
| Note levels are usually < 15mcg/g of stool in pancreatic insufficient CF patients. | ||||||||
| Normal faecal elastase levels are expected in infants born at term and by 2 weeks of age in infants born at less than 28 weeks gestation. Note at 6 weeks of age 60% of infants with CF are likely to be pancreatic insufficient and this rises to 90% by 1 year of age. Enteric coated acid resistant mini micro spheres and micro spheres are the product of choice - see table below. The efficacy of pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy is affected by such factors such as gut acidity and gastrointestinal transit time. Dose should be advised on an individual basis and requirements regularly reviewed by the dietician. Parents and patients should be educated on adjusting the dose and timing of pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy administration to achieve optimal absorption, growth and nutritional status. | ||||||||
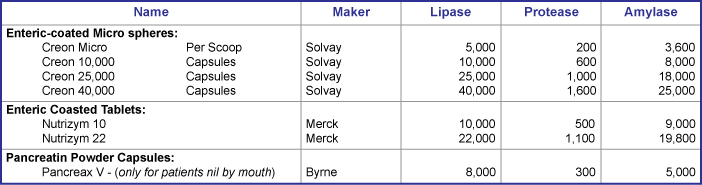 |
||||||||
**Note: dose should not generally exceed 10,000 units of lipase/kg body weight. |
||||||||
| Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Infants: | ||||||||
- |
Use mini micro spheres - Creon Micro or opened Creon 10,000. | |||||||
- |
Offer from a spoon sprinkled onto a little first stage apple puree. | |||||||
- |
Start with an initial doe of half a scoop of Creon Micro of a quarter of a scoop of Creon 10,000, per 90ml - 120ml of formula or breast feed - equivalent to 2,500 IU of lipase. | |||||||
- |
Spread the enzyme dose throughout the feed, offering some at the beginning, middle and end of the feed. | |||||||
- |
Note, check babies mouth for stray spheres at the end of the feed to avoid soreness. | |||||||
- |
Increase dose gradually in response to clinical symptoms, stools and weight gain - do not exceed 10,000 units of lipase/kg of body weight. | |||||||
- |
As weaning commences, adjust Creon dose according to fat content of meals and clinical symptoms. | |||||||
| Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Toddlers and Children: | ||||||||
- |
Initial dose of 1 - 2 Creon/meal and 1 creon per snack. | |||||||
- |
The dose needs to be worked out according to the individual and the fat content of the meal. | |||||||
- |
Children should be encouraged to swallow capsules whole at a young age, until this point is reached the enzymes should be offered from a spoon with a little fruit puree of fromage frais. They should not be sprinkled on the food. | |||||||
- |
They should not be chewed or crushed. | |||||||
- |
The enzymes should continue to be spread throughout the meal and dose adjusted according to symptoms of malabsorption. | |||||||
| Teenagers and Adults: | ||||||||
| If well established on pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy and high doses of enzymes required, consider changing to Creon 25,000 or Creon 40,000 to decrease the number of capsules needing to be taken. Please note that these preparations do not contain Eudragit in their enteric coating and hence are not associated with an increased risk of fibrosing colonopathy. | ||||||||
| Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy and Gastrostomy Feeds: | ||||||||
| Enzymes need to be taken with all types of feed, both elemental and polymeric, the dose being worked out according to the type and rate of feed plus the individuals requirements. In patients who are fed over night a reduced enzyme dose is usually required due to the stimulation of gastric lipase, a starting point i usually 1 - 2 capsules of the patients usual enzyme before and after the feed. Note that it is not necessary to wake the patient up during the night to give enzymes, The dose can then be adjusted according to symptoms. If bolus feeds are given or the feed is fed at a higher rate over a shorter time period then a higher dose may be required. | ||||||||
| Patients who are Nil By Mouth: | ||||||||
| E.g. a baby requiring NG feeding or a ventilated patient, powdered enzymes such as Pancrex V should be flushed down the tube at 3 - 4 hourly intervals. An acid blocking drug such as omeprazole should be prescribed as powdered enzymes are denatured by the acidity of the stomach. Enzymes should also be taken if the patient has to fast for any period of time to help break down the thick sticky mucus that may cause a blockage - suggesting 1 x Creon 10,000 every 3 - 4 hours. | ||||||||
| What to do if Malabsorption Persists: | ||||||||
- |
Check storage of enzymes - away from direct heat and sunlight. | |||||||
- |
Check the enzymes are in date. | |||||||
- |
Are the enzymes being administered in the correct way - spread out throughout the meal. | |||||||
- |
Are there any compliance issues and what can be done to encourage patients. | |||||||
- |
Proton pump inhibitors or H2 antagonists reduce gastric acid and may improve absorption. | |||||||
- |
Is the patient receiving antibiotics which may affect the efficacy and balance of stool. | |||||||
| Other Investigations if Malabsorption continues: | ||||||||
- |
Stool analysis to look for the presence of fat droplets - cytology. | |||||||
- |
Coeliac Screen | |||||||
- |
Consider lactose deficiency. | |||||||
- |
Microbiological assay of stool - MC&S, OCP | |||||||
| References: | ||||||||
1, |
CF Trust Nutritional Management of Cystic Fibrosis, 2002 | |||||||
2, |
Clinical Guidelines for the Care of Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Royal Brompton & Harefield NHS Trust, 2007. | |||||||
3, |
Cystic Fibrosis in Children and Adults. The Leeds Method of Management, 2008. | |||||||
| Dowloadable PDF File - PDF File | ||||||||
Document approved - 2011 |
||||||||
Document due for review - December 2013 |
||||||||
| Acknowledgements: The Peninsula CF team acknowledges the use of guidelines produced by The CF Trust, Manchester, Papworth, Leeds and Brompton CF teams during development of these local Peninsula protocols and guidelines. | ||||||||
| Disclaimer: While efforts have been made to ensure that all the information published on this web site is correct, the authors take no responsibility for the accuracy of information, or for harm arising as a consequence of errors contained within this web site. If you have concerns regarding treatment, drugs or doses then consult your local CF consultant. |
©2009 - 2013 All rights reserved. Peninsula Cystic Fibrosis Network |